Your Nodules in plants images are ready in this website. Nodules in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Nodules in plants files here. Download all free images.
If you’re looking for nodules in plants images information related to the nodules in plants topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Nodules In Plants. The available nitrogen in the the soil i.e higher the level of nitrogen the lesser is the formation of root nodules due to the luxury consumption. Some higher plants, and some. Nescent nodules are usually greyish green or brown in‐ side. Within the nodule, the nitrogen fixing bacteria are able to convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which supplies the nitrogen required for bacterial and plant growth.
Pollinators On The Brain Rhizobia and Root Nodules From pollinatorsonthebrain.blogspot.com
The bacteria live in the plant cells, located on the root, and form nodules. Nitrogen fixation by legumes is. Root nodules are found in plants belonging to the family fabaceae or leguminosae. Glauca, the prenodule represents a very simple symbiotic organ where both frankia and plant cells differentiate into their symbiotic condition. Before considering the engineering of a fully developed symbiotic. Nodules provide a suitable environment for the nitrogenase enzyme complex of bacteria to convert
However, this discussion is restricted to nodules in vascular plants, including tomato (lycopersicon esculentum, 2n = 24) on which we have done most of our work.
Crenata, or coral berry, which is widely cultivated for ornamental uses. The first description of the bacterial leaf nodule and most of leaf nodule symbiosis studies were demonstrated in a. The root nodule is the selective symbiont between legumes and leguminous bacteria. Both (b) and (c) medium. Diffusion resistance of nodules attached to intact plants maintained in controlled conditions (minchin, witty, and sheehy, 1983a; (2000a) showed that, in the actinorhizal plant c.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
Nodules showed a smaller average diameter and average dry weight per nodule than toyosuzu regardless of plant age or rhizobial strains (bradyrhizobium japonicum (ai017, j5033, 646, jlb140), b. Rhizobia bacteria can convert nitrogen gas (n 2 ) to ammonia (nh 3 ) in a process called nitrogen fixation. The available nitrogen in the the soil i.e higher the level of nitrogen the lesser is the formation of root nodules due to the luxury consumption. They include leguminous plants like beans, peas, peanuts etc. Formation of root nodules some important questions q:
 Source: sbar.arizona.edu
The number and intensity of formation of root nodule is effected by following factors : Nodules showed a smaller average diameter and average dry weight per nodule than toyosuzu regardless of plant age or rhizobial strains (bradyrhizobium japonicum (ai017, j5033, 646, jlb140), b. The number and intensity of formation of root nodule is effected by following factors : The number and intensity of formation of root nodule is effected by following factors : Nescent nodules are usually greyish green or brown in‐ side.
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
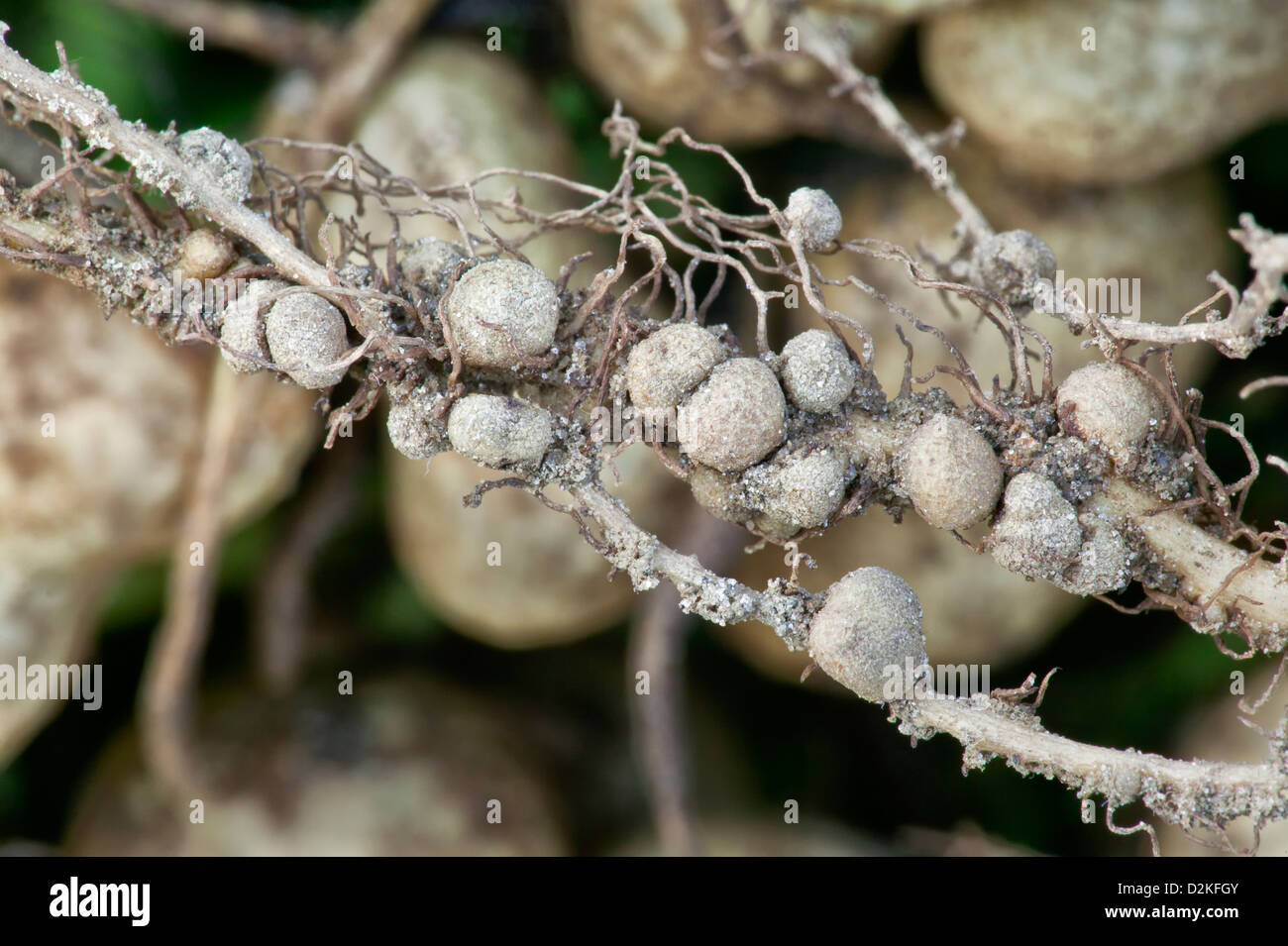
Nodules are formed because of the symbiotic relationship present between the leguminous plants and nitrogen fixing bacteria rhizobium which is the host bacteria. Within the nodule, the nitrogen fixing bacteria are able to convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which supplies the nitrogen required for bacterial and plant growth. Diffusion resistance of nodules attached to intact plants maintained in controlled conditions (minchin, witty, and sheehy, 1983a; Glauca, the prenodule represents a very simple symbiotic organ where both frankia and plant cells differentiate into their symbiotic condition. About 90% of legumes can become nodulated.
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
Although nodule primordium formation does not involve prenodule cells, laplaze et al. Although nodule primordium formation does not involve prenodule cells, laplaze et al. In autumn and at plant maturity (after flowering), the roots and nodules Nodules are formed because of the symbiotic relationship present between the leguminous plants and nitrogen fixing bacteria rhizobium which is the host bacteria. Nitrogen fixation in the nodule is very oxygen sensitive.
 Source: nagwa.com
Source: nagwa.com
Root nodules are found in plants belonging to the family fabaceae or leguminosae. The available nitrogen in the the soil i.e higher the level of nitrogen the lesser is the formation of root nodules due to the luxury consumption. • the purpose of the enterprise is to involve third world countries in mining nodules and give. In autumn and at plant maturity (after flowering), the roots and nodules In legumes and a few other plants, the bacteria live in small growths on the roots called nodules.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Host plant and the plant furnishes nutrients and energy for the activities of the bacterium. The number and intensity of formation of root nodule is effected by following factors : Some higher plants, and some. Host plant and the plant furnishes nutrients and energy for the activities of the bacterium. In autumn and at plant maturity (after flowering), the roots and nodules
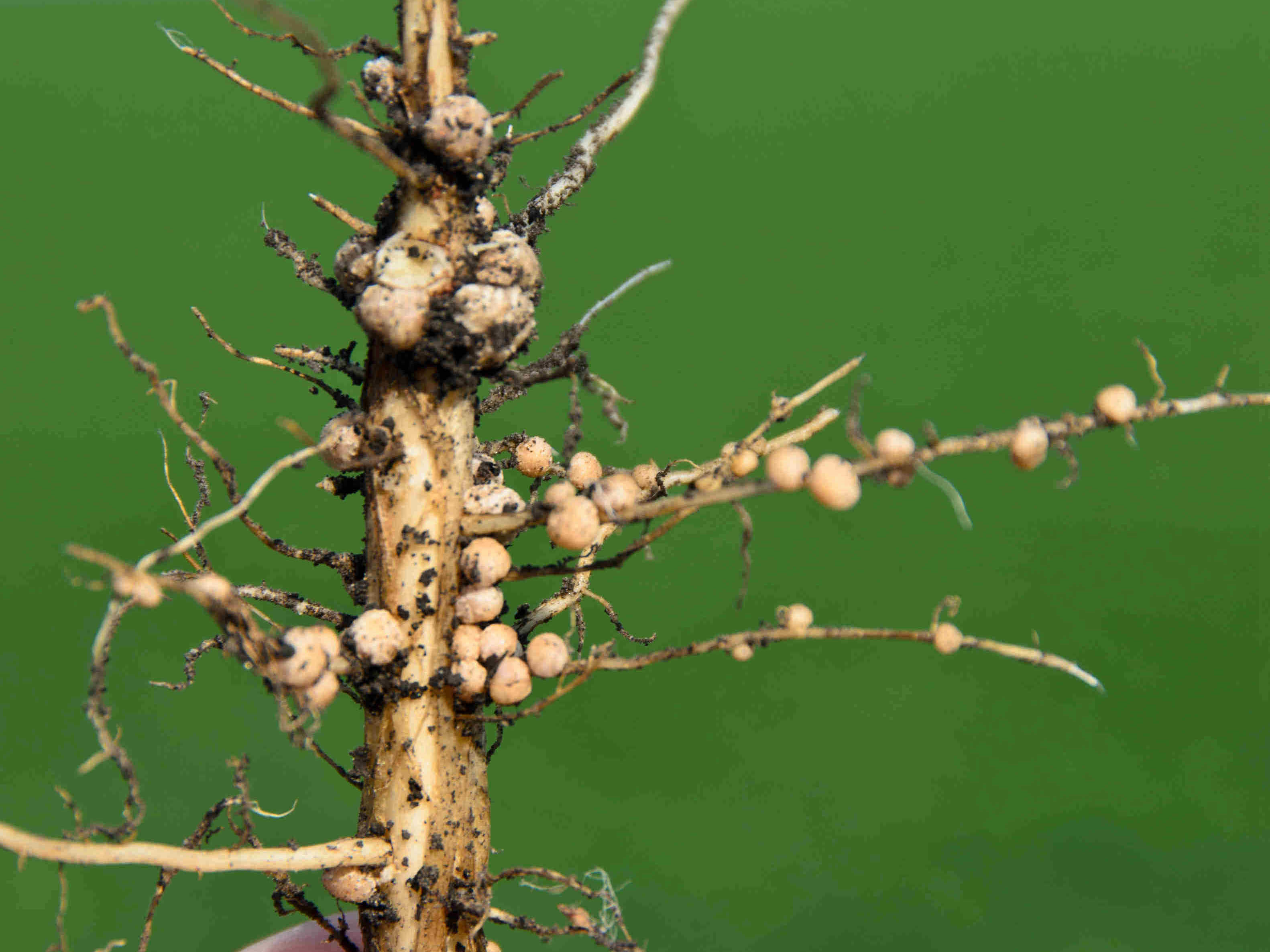 Source: news.cgtn.com
Source: news.cgtn.com
The first description of the bacterial leaf nodule and most of leaf nodule symbiosis studies were demonstrated in a. Some higher plants, and some. Nodules in soybean plant experts the fixed nitrogen in the form of. Rhizobia bacteria can convert nitrogen gas (n 2 ) to ammonia (nh 3 ) in a process called nitrogen fixation. The available nitrogen in the the soil i.e higher the level of nitrogen the lesser is the formation of root nodules due to the luxury consumption.
 Source: lookfordiagnosis.com
Source: lookfordiagnosis.com
Free living rhizobia cannot fix nitrogen and they have a different shape from the bacteria found in root nodules. In legumes and a few other plants, the bacteria live in small growths on the roots called nodules. Maximum nitrogen fixation around flowering nodules appear 4 to 6 weeks after sowing and reach maximum activity around flowering. Diffusion resistance of nodules attached to intact plants maintained in controlled conditions (minchin, witty, and sheehy, 1983a; However, root nodules are usually numerous and well distributed, consequently there is a paucity of data concerning their
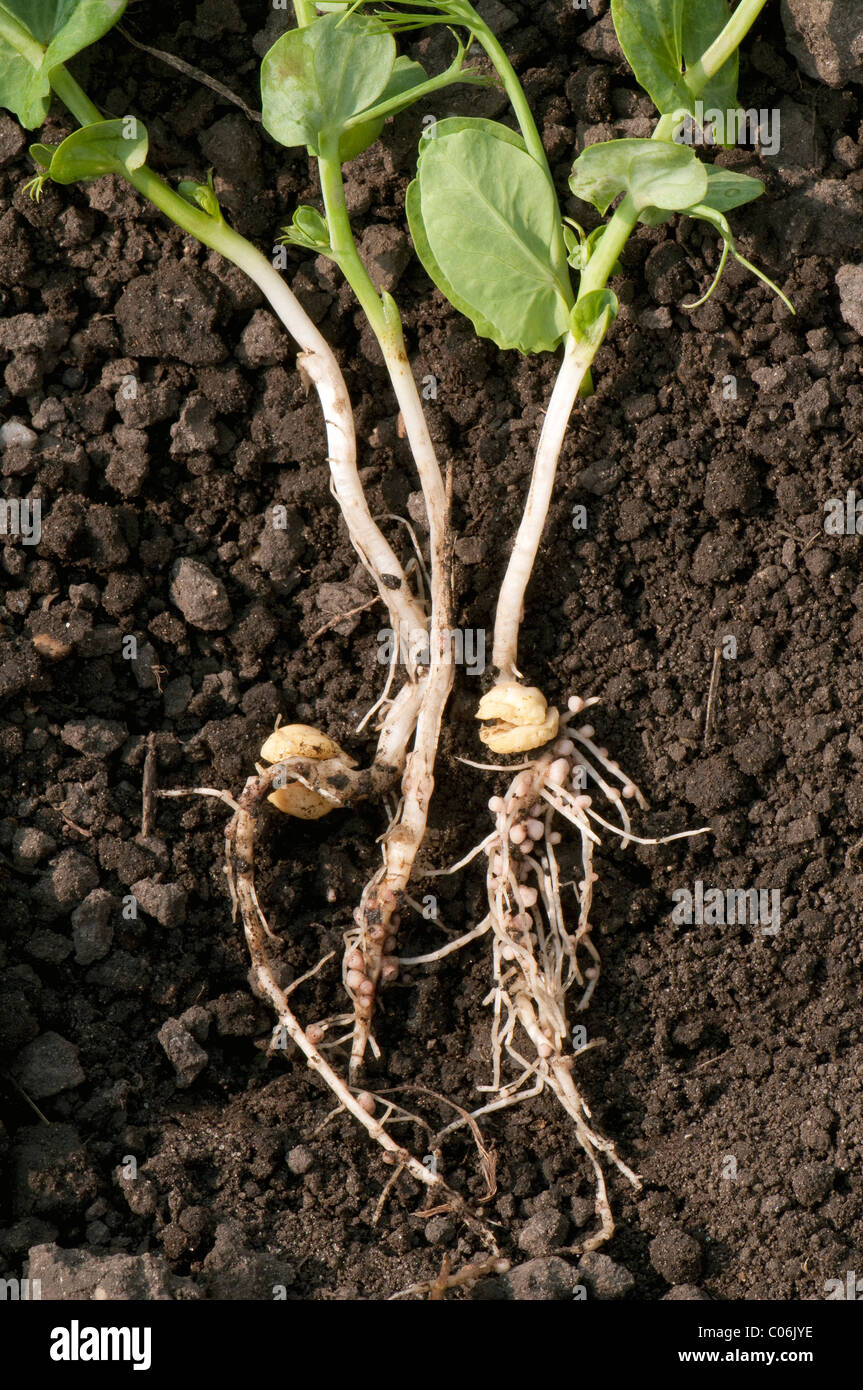 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
Associations ( symbiosis ) with. The root nodule is the selective symbiont between legumes and leguminous bacteria. Glauca, the prenodule represents a very simple symbiotic organ where both frankia and plant cells differentiate into their symbiotic condition. About 90% of legumes can become nodulated. Nitrogen fixation by legumes is.
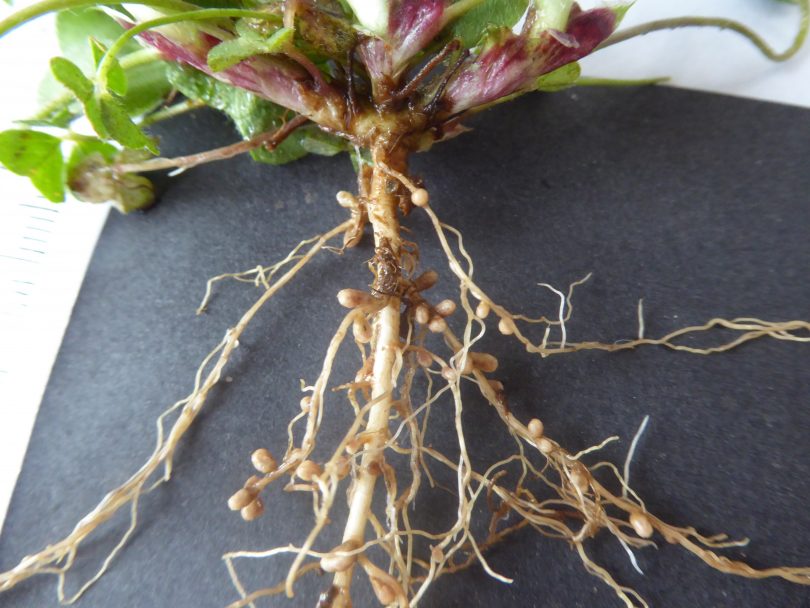 Source: aboutregional.com.au
Source: aboutregional.com.au
Glauca, the prenodule represents a very simple symbiotic organ where both frankia and plant cells differentiate into their symbiotic condition. The nodule also provides an environment with a low o 2 content, which is vital because nitrogenase, the enzyme that catalyzes biological nitrogen fixation, is denatured by o 2. Although nodule primordium formation does not involve prenodule cells, laplaze et al. • the purpose of the enterprise is to involve third world countries in mining nodules and give. Associations ( symbiosis ) with.
Source: pollinatorsonthebrain.blogspot.com
Associations ( symbiosis ) with. Do legumes add nitrogen to soil? The bacteria live in the plant cells, located on the root, and form nodules. Nodules have been observed in association with the synaptonemal complex (sc) in a wide variety of eukaryotic organisms (see carpenter 1979 and subsequently many other reports). Nodules provide a suitable environment for the nitrogenase enzyme complex of bacteria to convert
 Source: beyondthehumaneye.blogspot.com
Source: beyondthehumaneye.blogspot.com
Do legumes add nitrogen to soil? In legumes and a few other plants, the bacteria live in small growths on the roots called nodules. However, this discussion is restricted to nodules in vascular plants, including tomato (lycopersicon esculentum, 2n = 24) on which we have done most of our work. Tomato is well suited for. Some higher plants, and some.
Source: sevenandhalfsaturn.blogspot.com
The number and intensity of formation of root nodule is effected by following factors : However, root nodules are usually numerous and well distributed, consequently there is a paucity of data concerning their A nodule is a unique organ commonly found on the plant root where nitrogen fixing activities occur. Nodules are generally found on the roots of leguminous plants like beans, peas etc. Nitrogen fixation by legumes is.
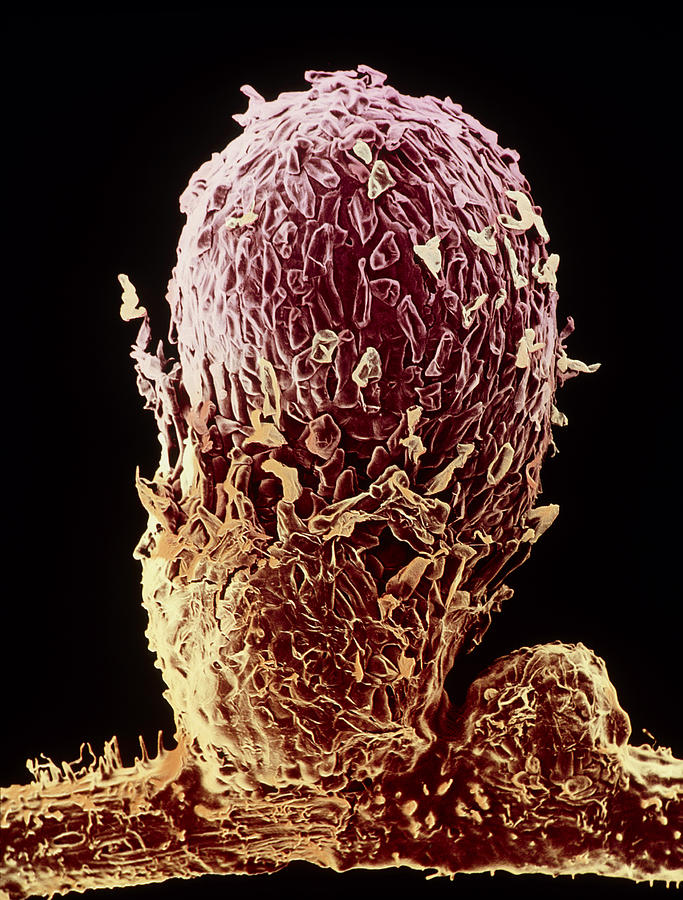 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Nodules showed a smaller average diameter and average dry weight per nodule than toyosuzu regardless of plant age or rhizobial strains (bradyrhizobium japonicum (ai017, j5033, 646, jlb140), b. The nodule is a specialized organ or outgrowth on the roots of the host plant, especially those of the family fabaceae (leguminosae), that contains bacteria preferably rhizobium. The bacteria live in the plant cells, located on the root, and form nodules. The number and intensity of formation of root nodule is effected by following factors : Nodules are formed because of the symbiotic relationship present between the leguminous plants and nitrogen fixing bacteria rhizobium which is the host bacteria.
 Source: naturphilosophie.co.uk
Source: naturphilosophie.co.uk
The nodule also provides an environment with a low o 2 content, which is vital because nitrogenase, the enzyme that catalyzes biological nitrogen fixation, is denatured by o 2. Root nodules are found in plants belonging to the family fabaceae or leguminosae. Rhizobia bacteria can convert nitrogen gas (n 2 ) to ammonia (nh 3 ) in a process called nitrogen fixation. The nodule is a specialized organ or outgrowth on the roots of the host plant, especially those of the family fabaceae (leguminosae), that contains bacteria preferably rhizobium. Tomato is well suited for.
 Source: robbinsfarmgarden.org
Source: robbinsfarmgarden.org
Nodules showed a smaller average diameter and average dry weight per nodule than toyosuzu regardless of plant age or rhizobial strains (bradyrhizobium japonicum (ai017, j5033, 646, jlb140), b. Some higher plants, and some. Nodules in soybean plant experts the fixed nitrogen in the form of. However, root nodules are usually numerous and well distributed, consequently there is a paucity of data concerning their Nescent nodules are usually greyish green or brown in‐ side.
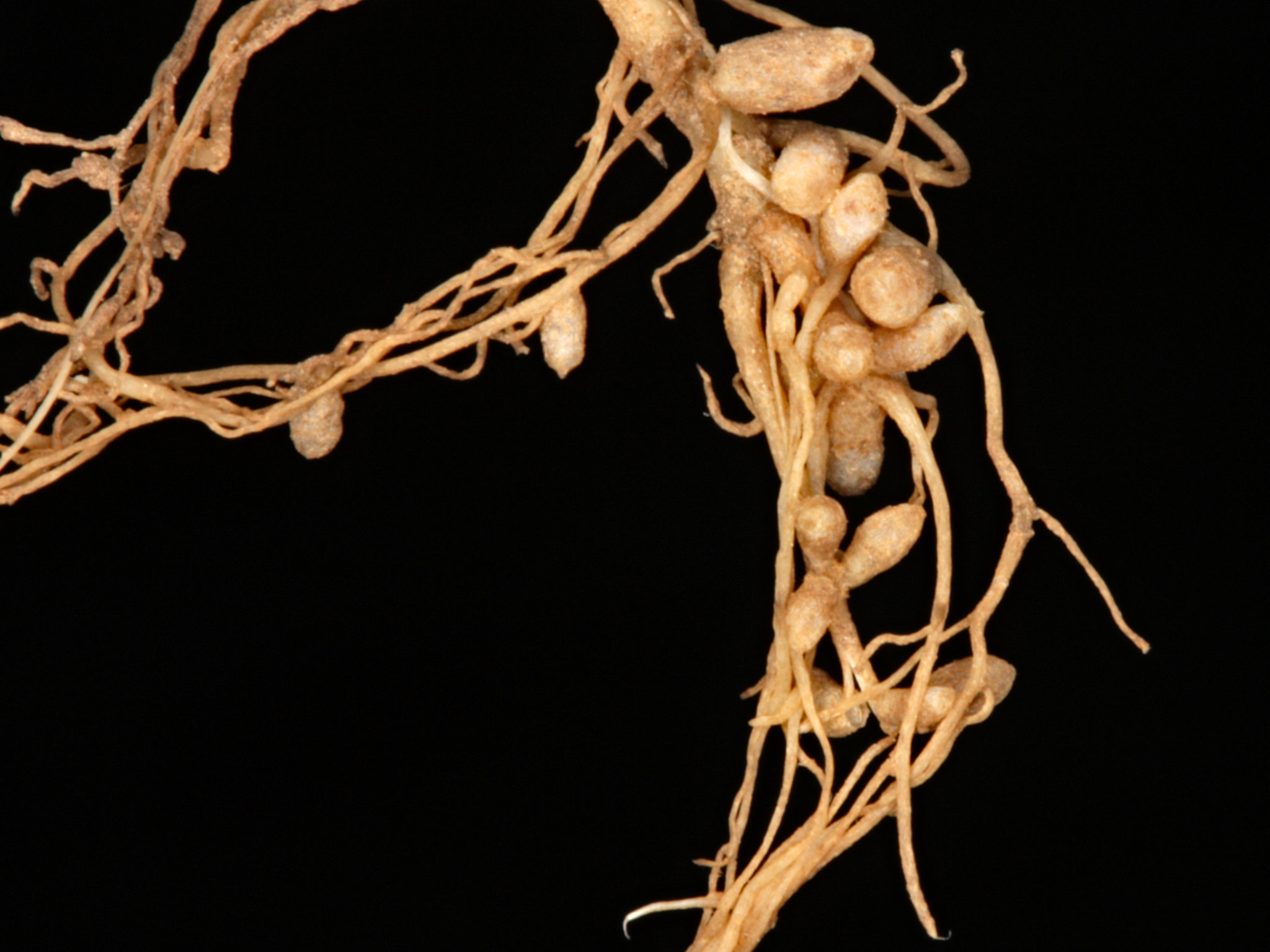 Source: richardmudhar.com
Source: richardmudhar.com
Do legumes add nitrogen to soil? Maximum nitrogen fixation around flowering nodules appear 4 to 6 weeks after sowing and reach maximum activity around flowering. Within the nodule, the nitrogen fixing bacteria are able to convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which supplies the nitrogen required for bacterial and plant growth. (2000a) showed that, in the actinorhizal plant c. However, this discussion is restricted to nodules in vascular plants, including tomato (lycopersicon esculentum, 2n = 24) on which we have done most of our work.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
Within the nodule, the nitrogen fixing bacteria are able to convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia which supplies the nitrogen required for bacterial and plant growth. The first step of nodule formation starts with the leguminous bacterium receiving a signal from the host plant. The nodule is a specialized organ or outgrowth on the roots of the host plant, especially those of the family fabaceae (leguminosae), that contains bacteria preferably rhizobium. Some higher plants, and some. The available nitrogen in the the soil i.e higher the level of nitrogen the lesser is the formation of root nodules due to the luxury consumption.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title nodules in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







